Quality that can stand the heat
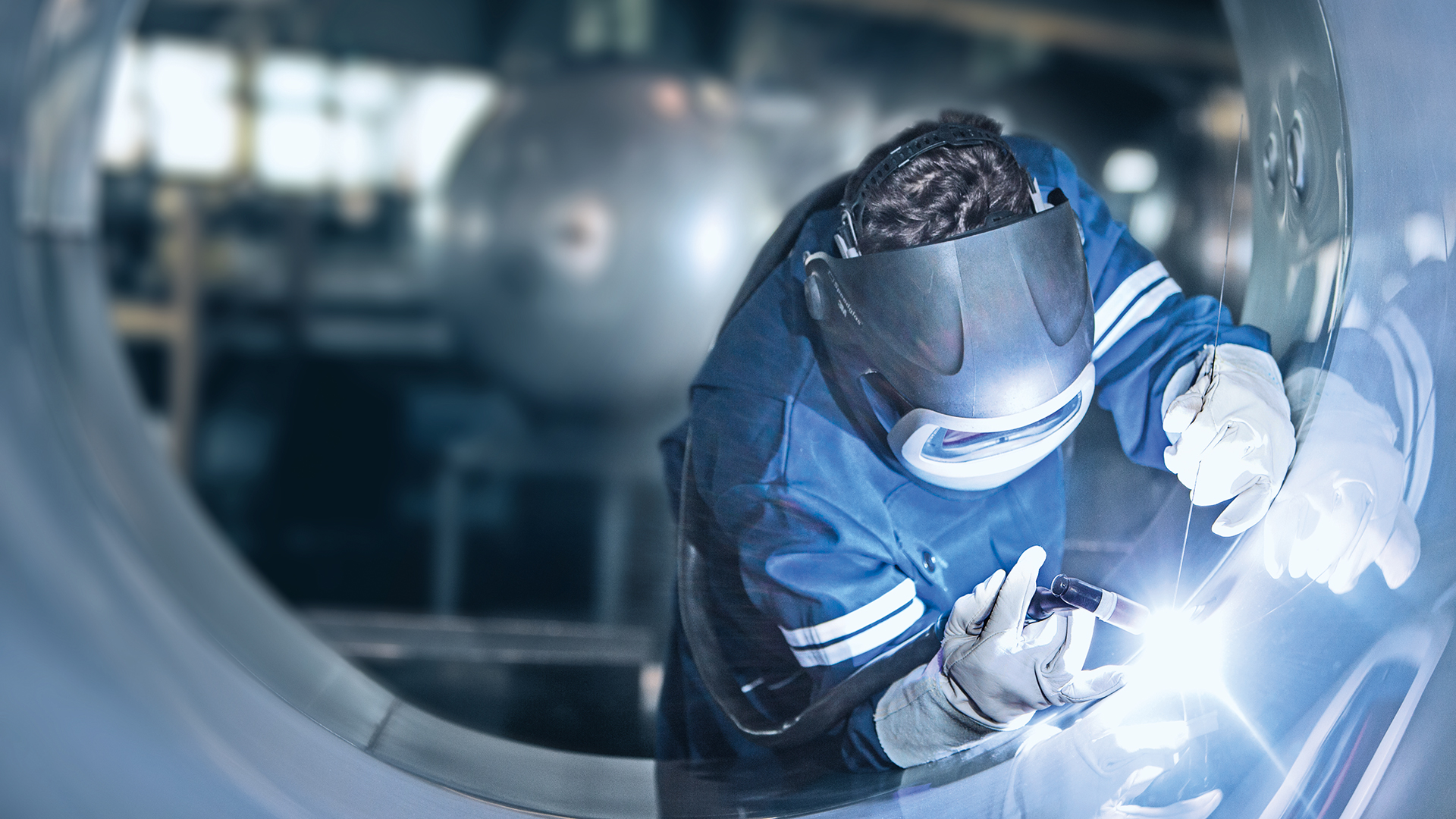
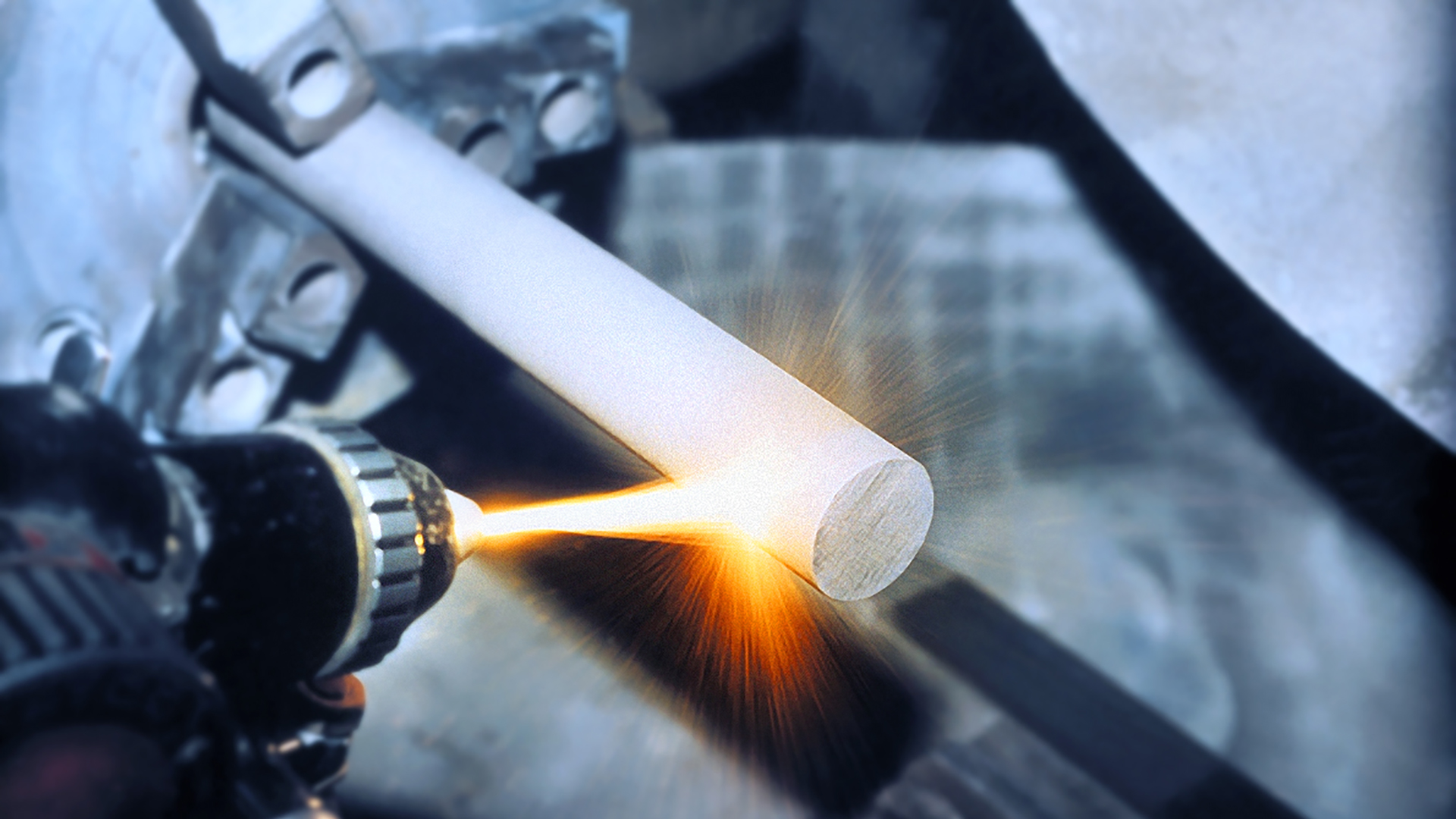
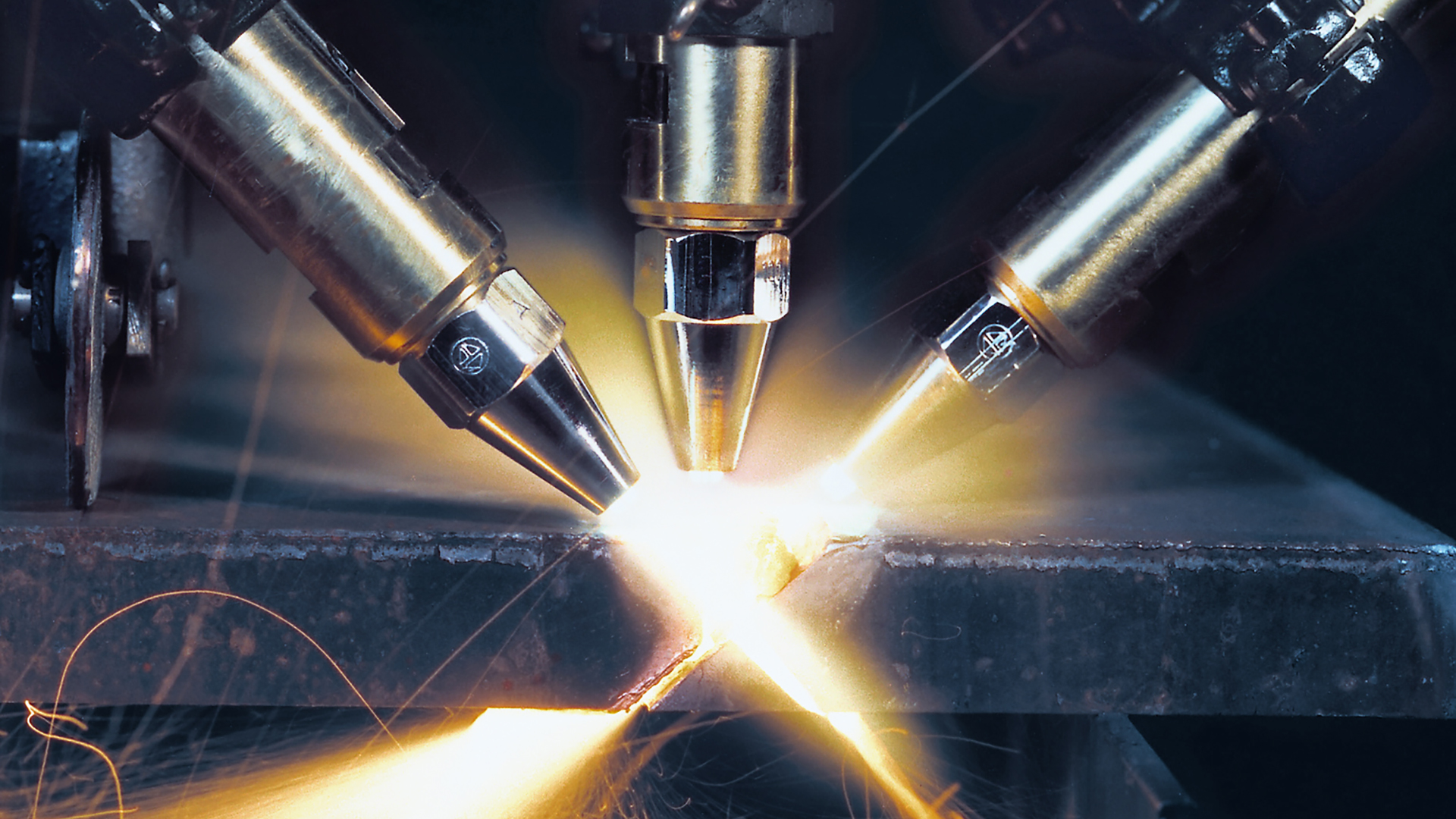
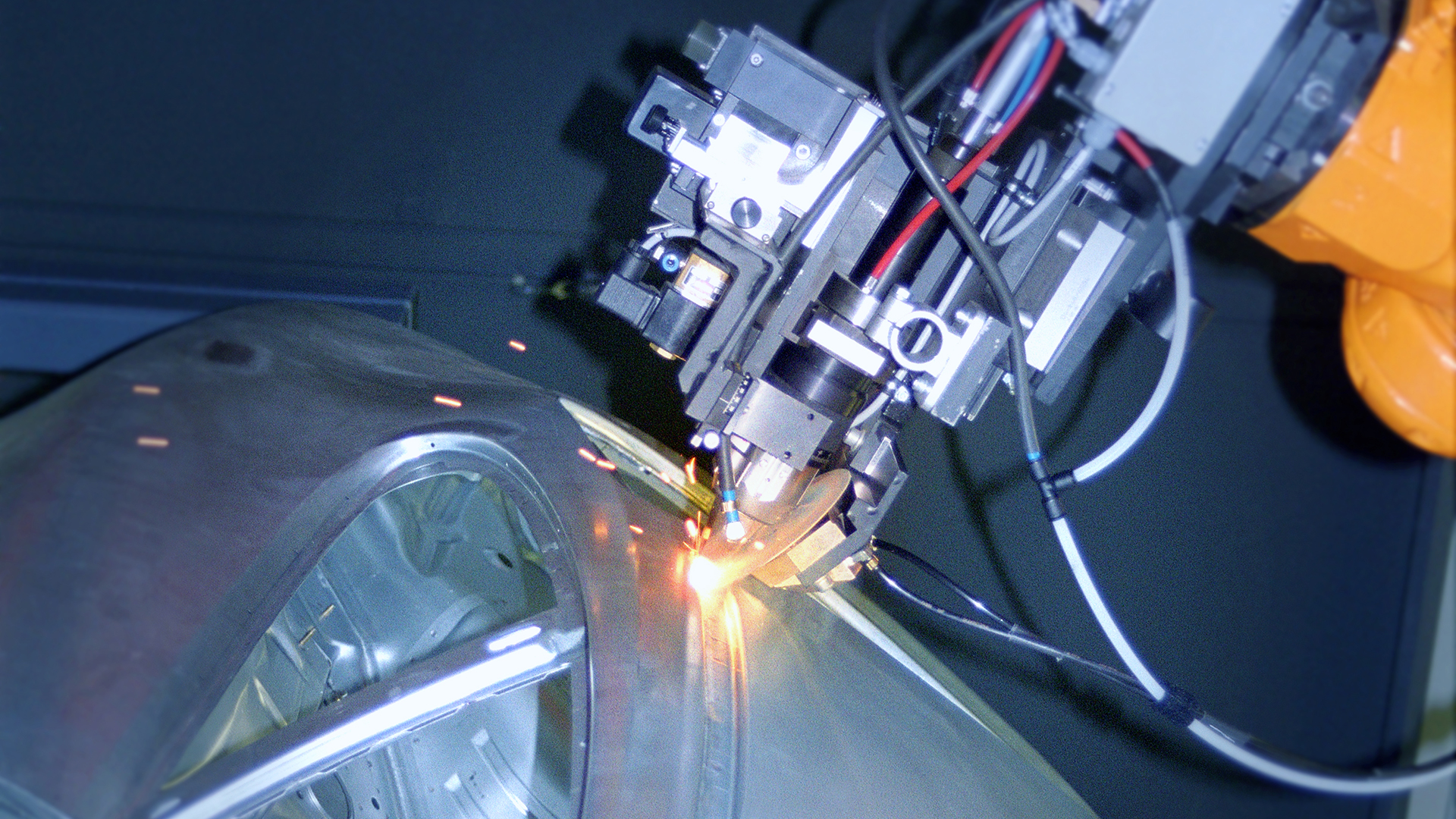
Welding technology covers a very wide range of procedures. The DIN EN 4063 standard defines well over 100 different welding methods. The range of gases and applications that Messer offers you in this area is correspondingly diverse.
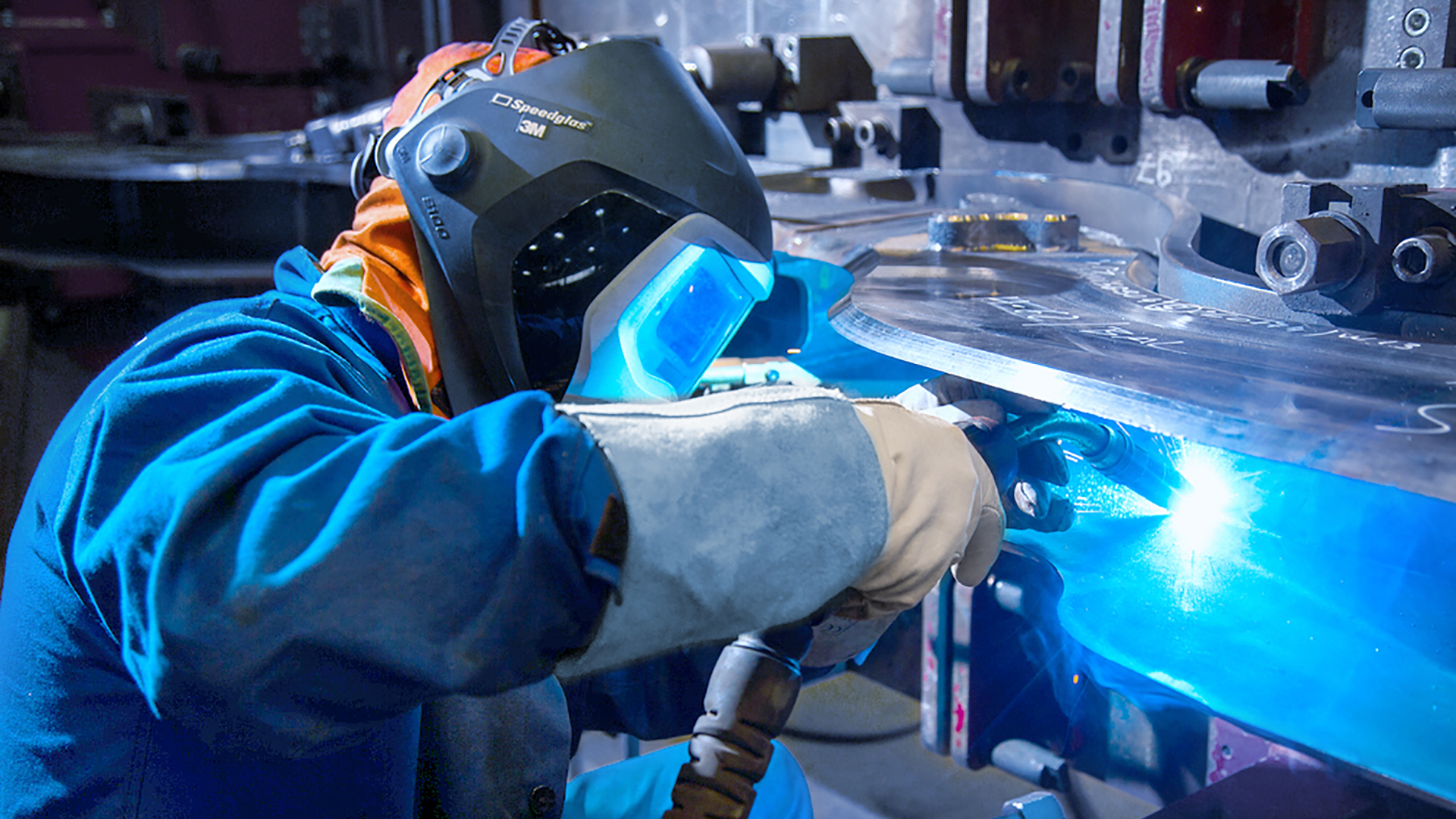
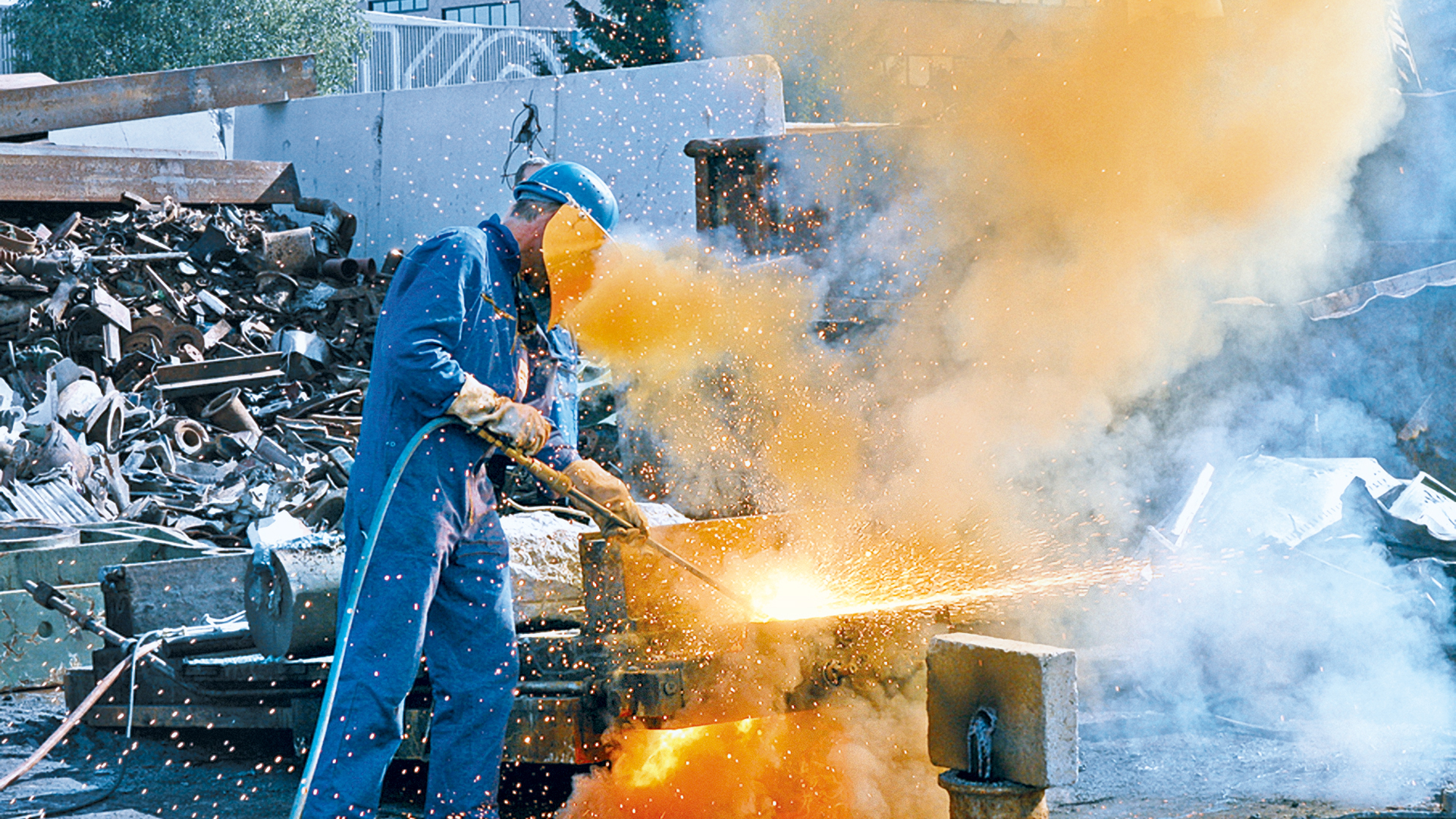
Shielding gases for welding are typically used in oxyfuel processes, which use fuel gas/air mixtures or, preferably, fuel gas/oxygen mixtures. Shielding gases for welding are also indispensable in arc welding, where the necessary thermal energy for the process comes from an arc. The same applies to TIG and MIG welding, where gas mixtures dominate today’s market. These mixtures feature a range of possible components, including argon and CO2 as well as oxygen, helium, hydrogen and nitrogen.
A great variety of these standardised gas mixtures is now available for the aforementioned applications. Messer sells its range of shielding gases for welding in a clearly structured system using standardised group-wide names that are based on the materials being worked:
Ferroline - Shielding gases for plain and low-alloy steels
Inoxline - Shielding gases for high-alloy steels and Ni-based alloys
Aluline - Shielding gases for aluminium and non-ferrous metals
As a manufacturer of industrial gases, we not only deal with those processes that involve the use of industrial gases, but also with processes that are in competition with this. Messer’s advisory service on shielding gases for welding will gladly show you which shielding gas is the right one for your application: in a personal consultation and through on-site demonstrations.
These procedures can be roughly divided into the following manufacturing processes:
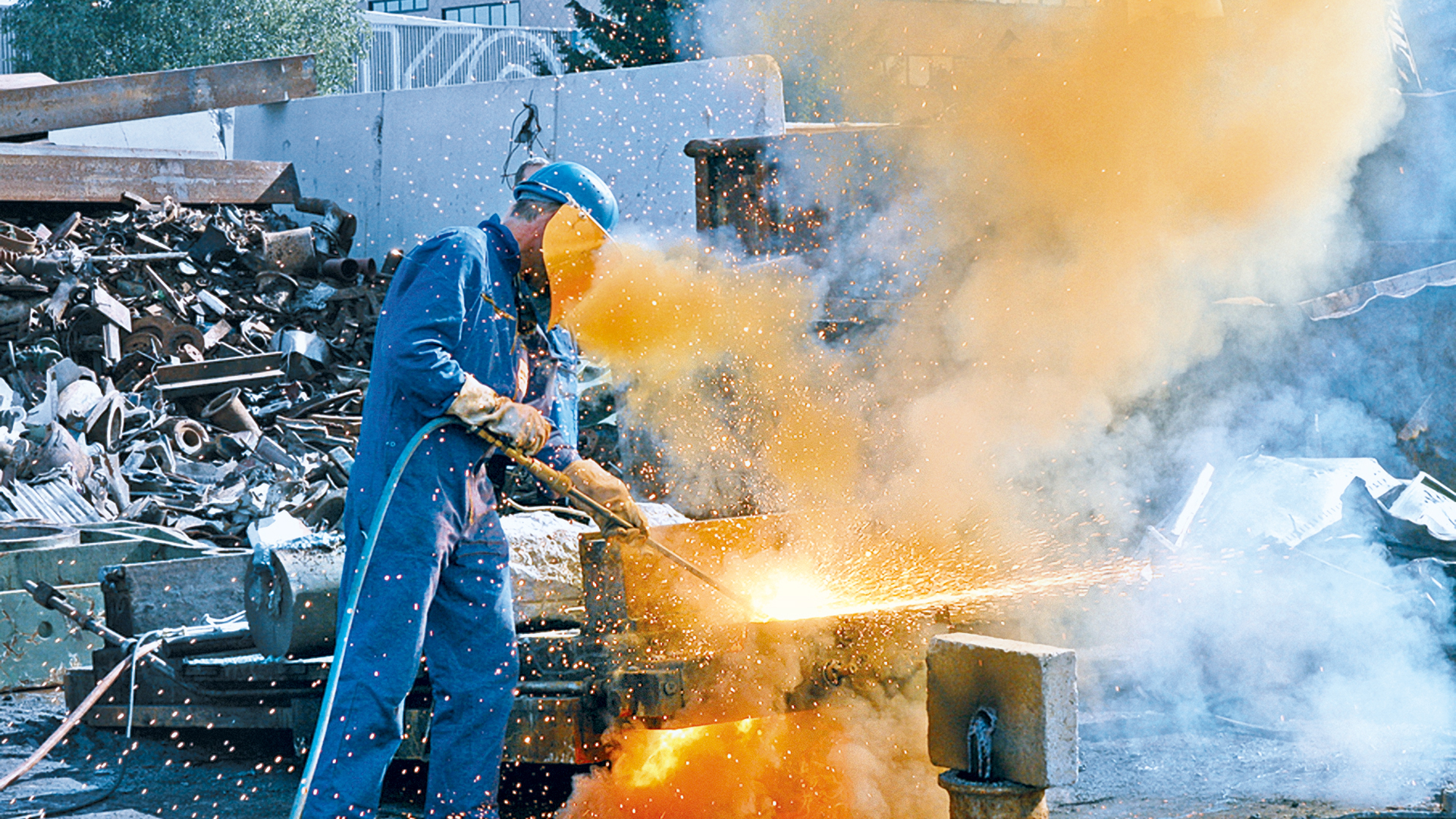
Cutting / Joining / Coating